Delving into What Causes Crohn’s Disease and How to Treat It Effectively, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a casual formal language style that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence.
This paragraph provides detailed information about the topic, setting the stage for an informative discussion.
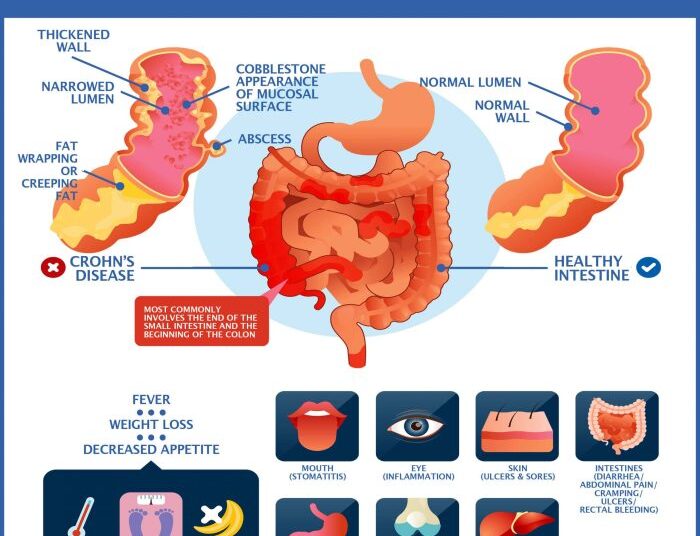
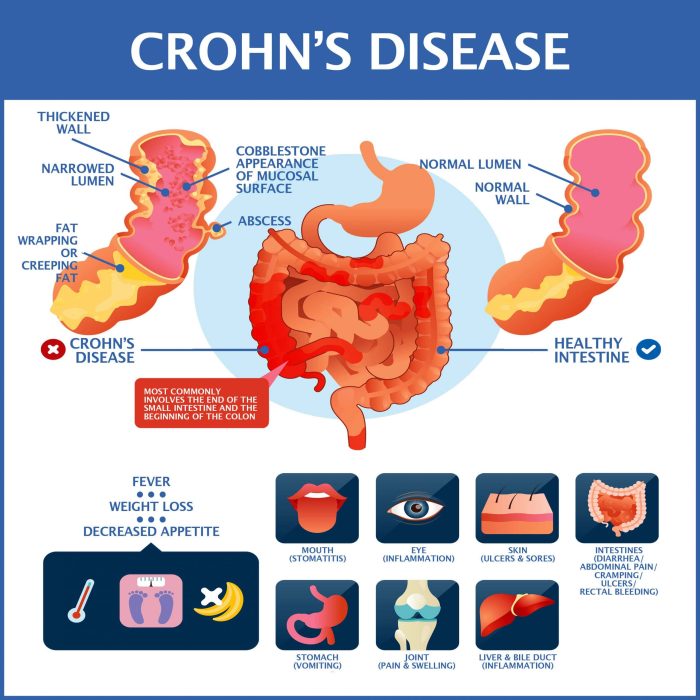
Causes of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the digestive tract. While the exact cause of Crohn’s disease is unknown, several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of Crohn’s disease. Individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Some genetic mutations have been linked to an increased susceptibility to Crohn’s disease.
Additionally, environmental factors such as diet, smoking, and exposure to certain bacteria or viruses can trigger the onset of the disease in genetically predisposed individuals.
Role of the Immune System
The immune system also plays a significant role in the development of Crohn’s disease. In individuals with Crohn’s disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. This abnormal immune response is thought to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Difference from Other Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Crohn’s disease is often confused with other inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis. While both conditions share some similarities, they affect different parts of the digestive tract and have distinct characteristics. Crohn’s disease can involve any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, and can cause inflammation in all layers of the intestinal wall.
In contrast, ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and only causes inflammation in the innermost lining of the colon.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is characterized by a variety of symptoms that can impact individuals differently. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and may occur in different parts of the digestive tract.
Common Symptoms
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Bloody stools
Varying Severity and Location
The severity of Crohn’s disease symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others may suffer from severe pain and complications. Additionally, the location of symptoms can differ, affecting various parts of the digestive tract such as the small intestine, colon, or rectum.
Impact on Quality of Life
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Chronic pain, frequent trips to the bathroom, and fatigue can interfere with daily activities, work, and relationships, leading to emotional distress and mental health issues.
Complications of Untreated Crohn’s Disease
- Intestinal strictures
- Fistulas
- Malnutrition
- Increased risk of colon cancer
- Perforation of the bowel
Diagnosis of Crohn’s Disease
When it comes to diagnosing Crohn’s disease, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the process involved, the tests and procedures used, as well as the challenges faced due to symptom overlap with other conditions.
Diagnostic Process for Identifying Crohn’s Disease
The diagnosis of Crohn’s disease typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. Gastroenterologists play a key role in the diagnostic process and may collaborate with other specialists depending on the specific symptoms and complications present.
Tests and Procedures Used to Diagnose Crohn’s Disease
Common tests and procedures used in the diagnosis of Crohn’s disease include colonoscopy, upper endoscopy, capsule endoscopy, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs, blood tests to check for inflammation and nutritional deficiencies, as well as stool tests to rule out infections or other gastrointestinal conditions.
Importance of Early Detection and Accurate Diagnosis
Early detection and accurate diagnosis of Crohn’s disease are essential to initiate timely treatment and prevent complications. A delay in diagnosis can lead to disease progression, increased severity of symptoms, and a higher risk of complications such as strictures, fistulas, or abscesses.
Challenges of Diagnosing Crohn’s Disease
One of the main challenges in diagnosing Crohn’s disease is its similarity in symptoms with other gastrointestinal disorders like ulcerative colitis or irritable bowel syndrome. This overlap can sometimes result in misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis, highlighting the importance of thorough evaluation by experienced healthcare providers.
Treatment Options for Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease can be managed through various treatment approaches, including medication, surgical intervention, and lifestyle modifications. Each of these options plays a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with Crohn’s disease.
Medication for Crohn’s Disease
- Medication is often the first line of treatment for Crohn’s disease and aims to reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Common medications used include anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, antibiotics, and biologic therapies.
- Medication can help control symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue, allowing individuals to lead more comfortable lives.
- It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most effective medication regimen for their specific condition.
Surgical Intervention for Crohn’s Disease
- Surgery may be necessary for individuals with severe Crohn’s disease complications, such as intestinal blockages, fistulas, or abscesses.
- While surgery is not a cure for Crohn’s disease, it can help improve quality of life and alleviate symptoms in certain cases.
- Potential risks of surgery include infection, bleeding, and the need for repeat surgeries in the future.
- It is crucial for patients to discuss the risks and benefits of surgery with their healthcare team to make informed decisions.
Lifestyle Modifications for Crohn’s Disease
- Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and improve digestive health.
- Avoiding trigger foods such as spicy foods, dairy, and high-fiber foods can help prevent flare-ups and manage symptoms.
- Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and getting an adequate amount of sleep are also important lifestyle modifications for individuals with Crohn’s disease.
- It is essential for patients to listen to their bodies, keep track of their symptoms, and make necessary adjustments to their lifestyle to effectively manage their condition.
End of Discussion

Concluding this discussion on What Causes Crohn’s Disease and How to Treat It Effectively, the summary delivers key insights and final thoughts in a captivating manner.
Quick FAQs
What are the potential factors that can trigger Crohn’s disease?
Potential triggers include genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction.
How do the symptoms of Crohn’s disease impact a person’s quality of life?
Symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life, affecting daily activities and overall well-being.
Why is early detection important in diagnosing Crohn’s disease?
Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of the disease, preventing complications and improving long-term outcomes.
What lifestyle modifications can help manage Crohn’s disease effectively?
Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers can assist in managing Crohn’s disease symptoms.